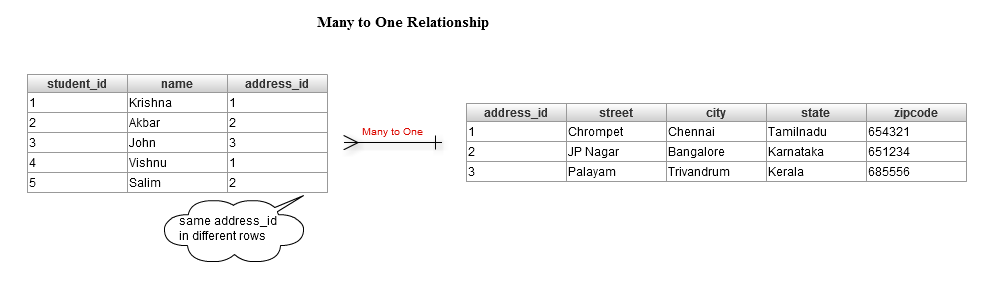
Many to One Mapping Annotation:
To link one entity to another, you need to map the association property as a to one association. In the relational model, you can either use a foreign key or an association table, or (a bit less common) share the same primary key value between the two entities.
To mark an association, use @ManyToOne.
@ManyToOne(cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
Student.java
package com.candidjava.hibernate;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "STUDENT")
public class Student {
private long studentId;
private String studentName;
private Address studentAddress;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String studentName, Address studentAddress) {
this.studentName = studentName;
this.studentAddress = studentAddress;
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name = "STUDENT_ID")
public long getStudentId() {
return this.studentId;
}
public void setStudentId(long studentId) {
this.studentId = studentId;
}
@Column(name = "STUDENT_NAME", nullable = false, length = 100)
public String getStudentName() {
return this.studentName;
}
public void setStudentName(String studentName) {
this.studentName = studentName;
}
@ManyToOne(cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
public Address getStudentAddress() {
return this.studentAddress;
}
public void setStudentAddress(Address studentAddress) {
this.studentAddress = studentAddress;
}
}Address.java
package com.candidjava.hibernate;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "ADDRESS")
public class Address {
private long addressId;
private String street;
private String city;
private String state;
private String zipcode;
public Address() {
}
public Address(String street, String city, String state, String zipcode) {
this.street = street;
this.city = city;
this.state = state;
this.zipcode = zipcode;
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name = "ADDRESS_ID")
public long getAddressId() {
return this.addressId;
}
public void setAddressId(long addressId) {
this.addressId = addressId;
}
@Column(name = "ADDRESS_STREET", nullable = false, length = 250)
public String getStreet() {
return this.street;
}
public void setStreet(String street) {
this.street = street;
}
@Column(name = "ADDRESS_CITY", nullable = false, length = 50)
public String getCity() {
return this.city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
@Column(name = "ADDRESS_STATE", nullable = false, length = 50)
public String getState() {
return this.state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
@Column(name = "ADDRESS_ZIPCODE", nullable = false, length = 10)
public String getZipcode() {
return this.zipcode;
}
public void setZipcode(String zipcode) {
this.zipcode = zipcode;
}
}save or inserting record into many to one annotation mapping
public void insertStudent(Student bk) {
try {
Session s = getSession();
Transaction transaction = s.beginTransaction();
s.save(bk);
// s.save(b);
transaction.commit();
} catch (HibernateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}Get or fetch record from many to one annotation mapping
public Student getStudent(long id) {
Student ls = new Student();
try {
Session s = getSession();
ls = (Student) s.load(Student.class, id);
// System.out.println(ls.size());
} catch (HibernateException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
return ls;
}Download