Many-to-Many Association Mapping Annotation
This tutorial shows you Many to many relationship hibernate example using Join table annotations
A many-to-many association is defined logically using the @ManyToMany annotation. You also have to describe the association table and the join conditions using the @JoinTable annotation.
@ManyToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinTable(name = "STUDENT_COURSE", joinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = "STUDENT_ID") }, inverseJoinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = "COURSE_ID") })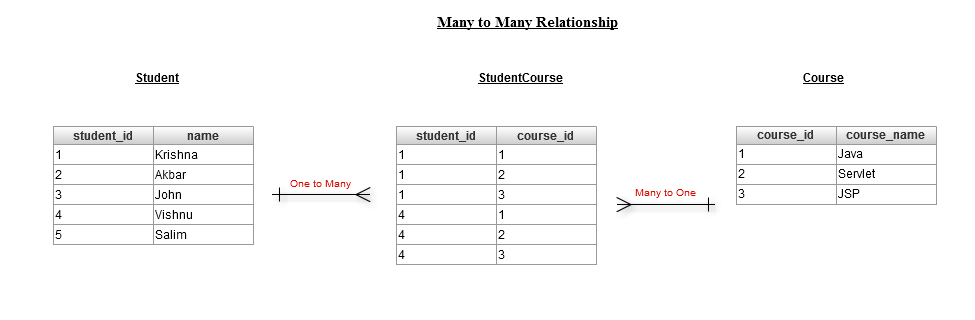
Student.java
package com.candidjava.hibernate;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.JoinTable;
import javax.persistence.ManyToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "STUDENT")
public class Student {
private long studentId;
private String studentName;
private Set<Course> courses = new HashSet<Course>(0);
public Student() {
}
public Student(String studentName) {
this.studentName = studentName;
}
public Student(String studentName, Set<Course> courses) {
this.studentName = studentName;
this.courses = courses;
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name = "STUDENT_ID")
public long getStudentId() {
return this.studentId;
}
public void setStudentId(long studentId) {
this.studentId = studentId;
}
@Column(name = "STUDENT_NAME", nullable = false, length = 100)
public String getStudentName() {
return this.studentName;
}
public void setStudentName(String studentName) {
this.studentName = studentName;
}
@ManyToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinTable(name = "STUDENT_COURSE", joinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = "STUDENT_ID") }, inverseJoinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = "COURSE_ID") })
public Set<Course> getCourses() {
return this.courses;
}
public void setCourses(Set<Course> courses) {
this.courses = courses;
}
}Course.java
package com.candidjava.hibernate;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "COURSE")
public class Course {
private long courseId;
private String courseName;
public Course() {
}
public Course(String courseName) {
this.courseName = courseName;
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name = "COURSE_ID")
public long getCourseId() {
return this.courseId;
}
public void setCourseId(long courseId) {
this.courseId = courseId;
}
@Column(name = "COURSE_NAME", nullable = false)
public String getCourseName() {
return this.courseName;
}
public void setCourseName(String courseName) {
this.courseName = courseName;
}
}save or inserting record into many to Many annotation mapping
public void insertStudent(Student bk) {
try {
Session s = getSession();
Transaction transaction = s.beginTransaction();
s.save(bk);
transaction.commit();
} catch (HibernateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}Get or fetch record from many to Many annotation mapping
public Student getStudents(long id) {
Student sd = null;
try {
Session s = getSession();
sd = (Student) s.get(Student.class, id);
} catch (HibernateException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
return sd;
}
Download